

The concept of "Smart City" was born in the United States of America in reference to an ideal city with a high automation content, in which the role of "supporting infrastructures" is assigned to Information & Communication Technologies (ICT)*.
In the first half of the 2000s the idea of “Smart City” moves towards a socially inclusive city, which assigns the function of social, human and participation capital to software.
The city of Rio de Janeiro is implementing the first “Smart City” project worldwide, with a plan for the intelligent use of technologies, relating to the management of waste; the goal was to improve the quality of life of its citizens. In this context, the adjective “Smart” begins to be used to connote a city capable of guaranteeing the well-being of the population in its various dimensions, through the use of hardware and software together.
With reference to the current cities, a “Smart City” must be able to implement innovative urban planning strategies, responding to the needs of the future and therefore aimed at an “intelligent” management of every type of resource.
Definitely, to be "Smart" a city must:
being able to become economically sustainable and energy self-sufficient;
develop new models for urban mobility;
provide its citizens with a high quality of life;
be itself an innovative tool to combat poverty, inequality and unemployment.
It should be emphasized that, in order to guarantee sustainable development, a smart city must favor a circular economy model instead of a linear economy model. That is, a virtuous economic system that takes into consideration the reuse, sharing, repair, refurbishment and recycling of existing materials and products, with the aim of reducing waste and reducing the emission of those substances that are considered harmful to the health of people and the environment.
The European Parliament defines a "Smart City" as
a city with at least one initiative capable of addressing one or more of the following six characteristics:
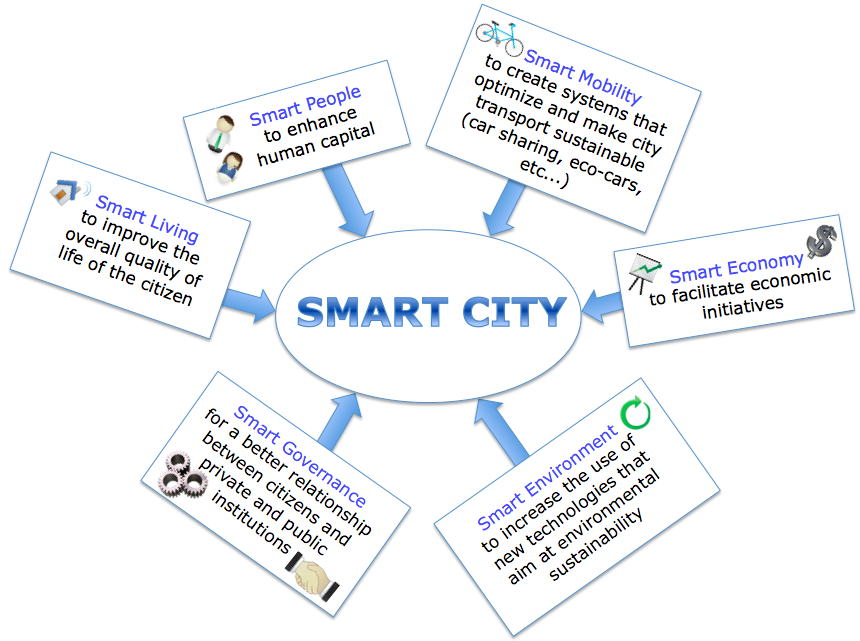

It is therefore possible to attribute the following adjectives to an "intelligent" city:
technological and interconnected, clean, attractive, reassuring, efficient, open, collaborative, creative, digital and green.
|
*ICT indicates the set of technologies and methods that provide access to information through telecommunications (TLC). The communication technologies referred to when talking about ICT are, for example: internet, radio, television, mobile phones, network hardware and software, satellite systems and also the various services and applications associated with these technologies, such as videoconferencing, distance learning, etc... Ultimately, it can be said that ICT refers to the set of information technologies and digital communication. |